Spread in forex trading
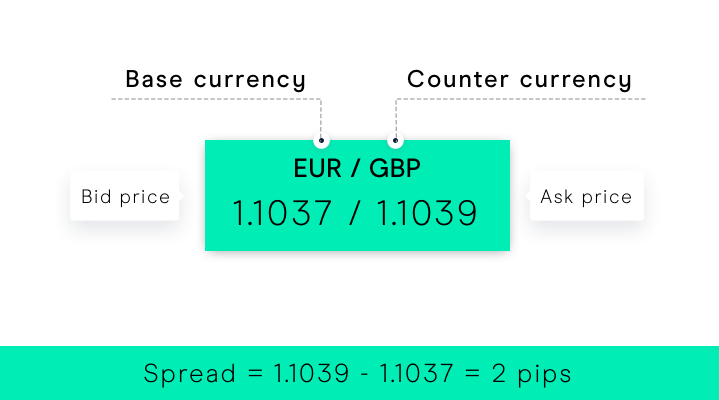
In forex trading, the spread is the difference between the bid (sell) price and the ask (buy) price of a currency pair. There are always two prices given in a currency pair, the bid and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which you can sell the base currency, whereas the ask price is the price you would use to buy the base currency.
The base currency is shown on the left of the currency pair, and the variable, quote or counter currency, on the right. The pairing tells you how much of the variable currency equals one unit of the base currency. The buy price quoted will always be higher than the sell price quoted, with the underlying market price being somewhere in-between.

What is spread in forex?
Most forex currency pairs are traded without commission, but the spread is one cost that applies to any trade that you place. Rather than charging a commission, all leveraged trading providers will incorporate a spread into the cost of placing a trade, as they factor in a higher ask price relative to the bid price. The size of the spread can be influenced by different factors, such as which currency pair you are trading and how volatile it is, the size of your trade and which provider you are using.
Some of the major major forex pairs include:
- EUR/USD: Euro and US dollar
- USD/JPY: US dollar and Japanese yen
- GBP/USD: British pound and US dollar
- USD/CHF: US dollar and Swiss franc
Forex trading pip spread
The spread is measured in pips, which is a small unit of movement in the price of a currency pair, and the last decimal point on the price quote (equal to 0.0001). This is true for the majority of currency pairs, aside from the Japanese yen where the pip is the second decimal point (0.01).
When there is a wider spread, it means there is a greater difference between the two prices, so there is usually low liquidity and high volatility. A lower spread on the other hand indicates low volatility and high liquidity. Thus, there will be a smaller spread cost incurred when trading a currency pair with a tighter spread.
When trading forex, the spread can either be variable or fixed. The spread for forex pairs is variable, so when the bid and ask prices of the currency pair change, the spread changes too. Some of the benefits and drawbacks of these two types of spreads are outlined below:
| Fixed Spread | Variable Spread |
|---|---|
| Could face requotes | No risk of requotes |
| Predictable transaction costs | Can get a tighter spread than fixed |
| Smaller capital requirements | Can reveal market liquidity |
| More appropriate for novice traders | More appropriate for experienced traders |
| A volatile market won't effect the spread | Spread can widen rapidly if there is high volatility |
| Likely to be exposed to slippage | Can be exposed to slippage |
Trade on over 330 forex pairs with us
How to calculate spread in forex
The spread is calculated using the last large numbers of the buy and sell price, within a price quote. The last large number in the image below is a 3 and a 4. When trading forex, or any other asset via a CFD trading or spread betting account, you pay the entire spread upfront. This compares to the commission paid when trading share CFDs, which is paid both when entering or exiting a trade. The tighter the spread, the better value you get as a trader.
For example:
The bid price is 1.26739 and the ask price is 1.26749 for the GBP/USD currency pair.
If you subtract 1.26739 from 1.26749, that equals 0.0001.
As the spread is based on the last large number in the price quote, it equates to a spread of 1.0.
- Practise trading the forex market risk-free with a demo account, using virtual funds.
- Start trading now with a live account to get access to exclusive features, such as our chart forum, live market data and Reuters/Morningstar reports, as well as stock trading.
What determines the spread in forex?
Factors that can influence the forex spread include market volatility, which can cause fluctuation. Major economic indicators, for example, can cause a currency pair to strengthen or weaken – thus affecting the spread. If the market is volatile, currency pairs can incur gapping, or the currency pair becomes less liquid, so the spread will widen.
Keeping an eye on our FX economic calendar can help prepare you for the possibility of wider spreads. By staying informed as to what events might cause currency pairs to become less liquid, you can make an educated prediction as to whether their volatility might increase, and thus whether you might see a greater spread. However, breaking news or unexpected economic data can be difficult to prepare for.
During the major forex market sessions, such as in London, New York and Sydney, there are likely to be lower spreads. In particular, when there is an overlap, such as when the London session is ending and the New York session is beginning, the spread can be narrower still. The spread is also influenced by the general supply and demand of currencies; if there is a high demand for the euro, the value will increase.

Forex spread trading strategies
Due to the above points, forex traders can employ an event-driven strategy based on macroeconomic indicators, in order to trade the tightest forex spreads and profit from opportune moments. For example, by monitoring the latest trading news and economic announcements, traders can expect changes in the forex market and find suitable entry and exit points when opening a position. This is called event-driven trading.
To start trading on some of the best currency pairs in the forex market, we have provided a list of suggestions here.
Forex spread indicator
A forex spread strategy can also be strengthened by the use of a trading indicator. The forex spread indicator is typically displayed as a curve on a graph to show the direction of the spread as it relates to bid and ask price. This helps visualise the spread in the forex pair over time, with the most liquid pairs having tighter spreads and the more exotic pairs having wider spreads.
There will also be a lower spread for currency pairs traded in high volumes, such as the major pairs containing the USD. These pairs have higher liquidity but can still be at risk of widening spreads if there is economic volatility.
Forex spread changes
If the forex spread widens dramatically, you run the risk of receiving a margin call, and worst case, being liquidated. A margin call notification occurs when your account value drops below 100% of your margin level, signalling you’re at risk of no longer covering the trading requirement. If you reach 50% below the margin level, all your positions may be liquidated.
It is therefore important to gauge how much forex leverage you’re trading with and the size of your position. Forex pairs are usually traded in larger amounts than shares, so it’s important to remain aware of your account balance.
Explore our forex spreads
Seamlessly open and close trades, track your progress and set up alerts
Low spread forex broker
We offer competitive spreads on a range of currency pairs, including major pairs such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, starting at just 0.7 pips, or a forex margin rate of 3.3%. Discover forex trading with our award-winning trading platform, Next Generation. We also offer forex trading on our hosted MetaTrader 4 platform. Get started now by opening an account.
Summary
A forex spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair, and is usually measured in pips. Knowing what factors cause the spread to widen is crucial when trading forex. Major currency pairs are traded in high volumes so have a smaller spread, whereas exotic pairs will have a wider spread. See our guide on money and risk management when trading in the forex market.